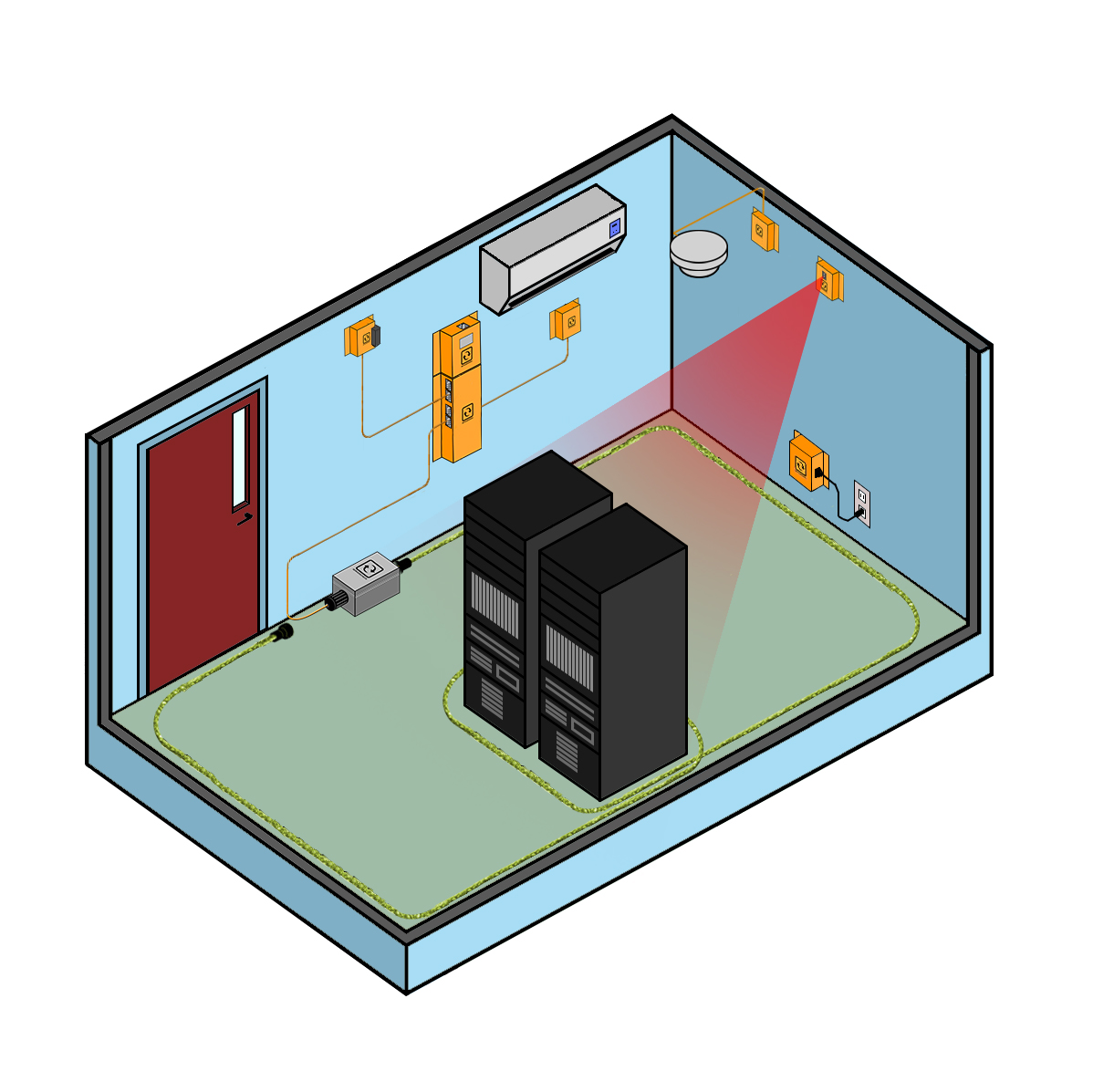
On this page you will find the standards recommended by ASHRAE for monitoring the environment in your data center or server room. The settings below apply to A1-A4 class data centers and server rooms. Environmental standards are provided for rack level monitoring, ambient monitoring and water leak detection.
| Application. | Location Of Sensors. | Settings. | Recommended Sensors. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ambient Room Temperature. | small rooms: center. data centers: potential hot zones. |
18-27°C / 64-80°F. | Temperature & Humidity Sensor | |
| Ambient Room Humidity. | Depending on size of the room: close to the door, center of room, center of racks and furthest point from door. | 40% - 60% rH. | Temperature & Humidity Sensor | |
| Rack Level Intake Temperature. | ASHRAE recommends 3 per rack: front (top, middle, bottom). | 18-27°C / 64-80°F. | Temperature Sensor | |
| Rack Level Outtake Temperature. | ASHRAE recommends 3 per rack: back (top, middle, bottom). | less than 20°C / 35°F difference from inlet temperature (typically <40°C / 105°F). | Temperature Sensor | |
| HVAC & Airco Monitoring. | Next to each HVAC unit to monitor their working state. |
settings depend on room to ensure 18-27°C temperature to rack and 40-60% rH at room level. | Temperature & Humidity Sensor | |
| Water Leak Detection | Under AC units, under raised floors and under any water pipe running through the room. | Water leak & Flooding Sensor |
1. Rack Level Monitoring
Summary: ASHRAE recommends no less than 6 temperature sensors per rack. However Gartner says that 3 could already be enough. Intake temperature should be between 18°-27°C / 64°-80°F. Outtake temperature should be less than 20°C / 35°F compared to the intake temperature.
Background Info:
Based on a recent Gartner study, the annual cost of a Wintel rack averages around $70,000 USD per year. This excludes the business cost of a rack. Risking losing business continuity or even your infrastructure due to environmental issues is not an option. But what are the environmental threats at a rack level?
A mistake often made is to only rely on monitoring the conditions at a room level and not at a rack level. The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) recommends no less than 6 temperature sensors per rack in order to safeguard the equipment. They should be mounted at the top, middle & bottom and this both at the front & back of rack.
When a heat issue arises, air conditioning units will initially try to compensate the problem. When you are doing temperature monitoring at a room level only, then the issue will only be detected when the air conditioning units are no longer capable of compensating the heat problem. It may be too late then... Rack temperature is also not server temperature.
A mistake often made is to only rely on monitoring the conditions at a room level and not at a rack level. The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) recommends no less than 6 temperature sensors per rack in order to safeguard the equipment. They should be mounted at the top, middle & bottom and this both at the front & back of rack.
When a heat issue arises, air conditioning units will initially try to compensate the problem. When you are doing temperature monitoring at a room level only, then the issue will only be detected when the air conditioning units are no longer capable of compensating the heat problem. It may be too late then... Rack temperature is also not server temperature.
As Gartner stated, you could already start at monitoring rack temperature with 3 measurement points: at the bottom front of the rack to verify the temperature of the cold air arriving to the rack (combined with airflow monitoring); at the top front of the rack to verify if all cold air gets to the top of the rack; and finally one at the top back of the rack which is typically the hottest point of the rack. Intake temperature should be between 18°-27°C / 64°-80°F. Outtake temperature should be less than 20°C / 35°F compared to intake temperature.
What is the impact of temperature on your systems? High end systems have auto shutdown capabilities to safeguard themselves against failures when temperature is too high. But did you know that CPU level errors and as such errors in your applications can be temperature induced? On top of that heat will stress fan equipment even more. This reduces equipment life time expectance. All this affects your system's availability and your business continuity.
For small rooms it is recommended to go with wired sensors. In larger data centers where you need a lot of monitoring points, daisy chain sensors can offer a cheaper alternative. With wireless sensors there is no cabling required. You'll also need substantially less IP addresses as 30 temperature sensors can talk to 1 base unit.

Background Info: Water leakage is a less known threat for server rooms & data centers. The fact that most data centers and server rooms have raised floors makes the risk even bigger as water seeks the lowest point.
Two type of sensors for water leakage can be commonly found: spot and water snake cable based. Spot sensors will trigger an alert when water touches the unit. Water rope or water snake cable sensors use a conductive cable whereby contact at any point on the cable will trigger an alert. The latter type is recommended over the first one due to its higher range and higher accuracy.
If using a raised floor, then one should consider putting the sensor under the raised floor as water seeks the lowest point.
The four main sources of water in a server room are:
The water leak sensors provided by InfraSensing can be daisy chained. This gives you a rope of up to 102m to monitor for water ingress. Need more than 30m? Simply add another sensor to your configuration. A base unit with the optional Sensorhub can support up to 8 water leak sensors for a total of almost 1km of leak detection.
All sensors connect to our SensorGateway (base unit). A base unit supports up to 2 wired sensors, or up to 8 with the optional sensor hub.
As defined by ASHRAE:
Class A1: Typically a data center with tightly controlled environmental parameters (dew point, temperature, and relative humidity) and mission critical operations; types of products typically designed for this environment are enterprise servers and storage products.
Class A2: Typically an information technology space or office or lab environment with some control of environmental parameters (dew point, temperature, and relative humidity); types of products typically designed for this environment are volume servers, storage products, personal computers, and workstations.
Class A3/A4: Typically an information technology space or office or lab environment with some control of environmental parameters (dew point, temperature, and relative humidity); types of products typically designed for this environment are volume servers, storage products, personal computers, and workstations.
What is the impact of temperature on your systems? High end systems have auto shutdown capabilities to safeguard themselves against failures when temperature is too high. But did you know that CPU level errors and as such errors in your applications can be temperature induced? On top of that heat will stress fan equipment even more. This reduces equipment life time expectance. All this affects your system's availability and your business continuity.
For small rooms it is recommended to go with wired sensors. In larger data centers where you need a lot of monitoring points, daisy chain sensors can offer a cheaper alternative. With wireless sensors there is no cabling required. You'll also need substantially less IP addresses as 30 temperature sensors can talk to 1 base unit.

2. Ambient room monitoring
Summary: Room monitoring, the temperature has to be maintained between should be between 18°-27°C / 64°-80°F. Humidity range is 40% and 60% rH. Dew point temperature should be 5.5ºC DP to 60% RH and 15ºC DP.
Background Info:
Ambient server room monitoring or data center monitoring is the environmental monitoring of the room for its humidity and temperature levels. Temperature and humidity sensors are typically deployed in:
potential “hot zones” inside the server room or data center
near air conditioning units to detect failure of such systems.
When multiple air conditioning systems are available in a room, then a failure of one system will initially be compensated by the others before it may lead to a total failure of the cooling system due to overload. As a result temperature / airflow sensors are recommended near each unit to get early failure detection.
When multiple air conditioning systems are available in a room, then a failure of one system will initially be compensated by the others before it may lead to a total failure of the cooling system due to overload. As a result temperature / airflow sensors are recommended near each unit to get early failure detection.
Monitoring humidity is equally important than temperature and often omitted. Did you know that the relative humidity (rH) in server rooms and data centers should be between 40% and 60% rH. Too dry will result in the build up of static electricity on the systems. Too humid and corrosion will start slowly damaging your equipment resulting in permanent equipment failures.
When using cold corridors inside the data center, then the ambient air temperature outside the corridor may be at higher levels. Air temperature of 37°C / 99°F are not uncommon in such setups. This allows to significantly reduce the energy cost. However this also means that temperature monitoring is of utmost importance as a failing air conditioning unit will have a way faster impact on the systems lifetime and availability (fans stress, CPU overheating, …) and running a room at higher temperatures may also affect non rack mounted equipment.
When using hot corridors it is important to monitor temperature across the room to ensure that sufficient cold air gets to each rack. In this case however one can also rely on rack based temperature sensors in addition of temperature and humidity sensors close to each air conditioning unit.
When using cold corridors inside the data center, then the ambient air temperature outside the corridor may be at higher levels. Air temperature of 37°C / 99°F are not uncommon in such setups. This allows to significantly reduce the energy cost. However this also means that temperature monitoring is of utmost importance as a failing air conditioning unit will have a way faster impact on the systems lifetime and availability (fans stress, CPU overheating, …) and running a room at higher temperatures may also affect non rack mounted equipment.
When using hot corridors it is important to monitor temperature across the room to ensure that sufficient cold air gets to each rack. In this case however one can also rely on rack based temperature sensors in addition of temperature and humidity sensors close to each air conditioning unit.

3. Water & Flooding Monitoring
Summary: Water leak sensors should be put around the perimeter of the room, under each AC unit and under each pipe running through the server room or data center.
Background Info: Water leakage is a less known threat for server rooms & data centers. The fact that most data centers and server rooms have raised floors makes the risk even bigger as water seeks the lowest point.
Two type of sensors for water leakage can be commonly found: spot and water snake cable based. Spot sensors will trigger an alert when water touches the unit. Water rope or water snake cable sensors use a conductive cable whereby contact at any point on the cable will trigger an alert. The latter type is recommended over the first one due to its higher range and higher accuracy.
If using a raised floor, then one should consider putting the sensor under the raised floor as water seeks the lowest point.
The four main sources of water in a server room are:
- leaking air conditioning systems: a water sensor should be placed under each AC unit
- water leaks in floors or roof above the room: water sensors should be put around the perimeter of the room at around 50cm/3ft from the outer walls and under the raised floor.
- leaks of water pipes running through server rooms: a water sensor should be placed under the raised floors
- traditional flooding: same as second point for water leaks from roof or above floors applies
The water leak sensors provided by InfraSensing can be daisy chained. This gives you a rope of up to 102m to monitor for water ingress. Need more than 30m? Simply add another sensor to your configuration. A base unit with the optional Sensorhub can support up to 8 water leak sensors for a total of almost 1km of leak detection.

4. Implementing standards with InfraSensing's SNMP and Modbus sensors
All sensors connect to our SensorGateway (base unit). A base unit supports up to 2 wired sensors, or up to 8 with the optional sensor hub.
| Application | Location | Setting | Part Number | Sensor Name | Rack Level Monitoring Sensors to monitor intake temperature | Front - Bottom of rack for room or floor cooling, top of rack for top cooling | 18-27°C / 64-80°F | ENV-TEMP or DAISY-TEMP | Wired or Wireless Temperature probes* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensors to monitor outtake temperature | Back - Top of rack (hot air climbs) | less than 20°C / 35°F difference from inlet temperature (typically <40°C / 105°F) | ENV-TEMP or DAISY-TEMP | Single or Daisy Chained Temperature probes* |
| Ambient Monitoring Temperature & humidity monitoring in server room | small server rooms: center of the room data centers: potential hot zones - furthest away from airco units | Temperature depends on type of room setup Humidity: 40-60% rH | ENV-THUM | Temperature & Humidity Sensor Probe* |
| Airconditioning Monitoring Early detection of failing air conditioning units | next to airco units | Temperature depends on setting of airco Humidity: 40-60% rH | ENV-THUM | Temperature & Humidity Sensor Probe* |
| Water Leaks / Flooding Detecting water leaks coming from outside of room | Around outside walls of server room / data center and under raised floor
best is to keep a 30-50cm / 10-20" from outer wall | ENV-W-LEAK-COMBO | Flooding Sensor Probe* with 6m/20ft water sensitive cable | |
| Detecting water leaks from air conditioning units | Under each air conditioning unit | ENV-W-LEAK-COMBO | Flooding Sensor Probe* with 6m/20ft water sensitive cable |
As defined by ASHRAE:
Class A1: Typically a data center with tightly controlled environmental parameters (dew point, temperature, and relative humidity) and mission critical operations; types of products typically designed for this environment are enterprise servers and storage products.
Class A2: Typically an information technology space or office or lab environment with some control of environmental parameters (dew point, temperature, and relative humidity); types of products typically designed for this environment are volume servers, storage products, personal computers, and workstations.
Class A3/A4: Typically an information technology space or office or lab environment with some control of environmental parameters (dew point, temperature, and relative humidity); types of products typically designed for this environment are volume servers, storage products, personal computers, and workstations.